Overview
E-mail may be accessed either through webmail within the control panel or remotely from a desktop client such as Outlook, Thunderbird, or Mail.
Important login information
Your login will always be user@domain for e-mail. For example, if your domain is example.com and your username myadmin, then the proper e-mail login is
myadmin@example.comand notmyadmin. Your password is the same password that is used to log into the control panel.Warning: 3 invalid logins in a 5 minute window will result in an automatic 10 minute blacklist. During this 10 minute window, you will not be able to access the e-mail server. This is a mechanism in place to reduce the likelihood of a successful brute-force attempt on your account.
Default Ports: |
Server: | Authentication: | Port: |
| SMTP Server (Outgoing Messages) | Non-Encrypted | AUTH | 25 (or 587) |
| Secure (SSL) | SSL | 465 | |
| IMAP Server (Incoming Messages) | Non-Encrypted | AUTH | 143 |
| Secure (SSL) | SSL | 993 | |
| POP3 Server (Incoming Messages) | Non-Encrypted | AUTH | 110 |
| Secure (SSL) | SSL | 995 |
Accessing via webmail
Webmail provides a convenient way to access e-mail from any web device. Webmail comes in 3 flavors that are accessible by different URLs and may be changed at any time. All of these webmail locations are also accessible within the control panel under Mail > Webmail.
- Horde is accessible via http://horde.<domain>
- Comprehensive mail client with address book, reminders, and filtering support
- SquirrelMail is accessible via http://mail.<domain>
- Lightweight client suitable for mobile devices
- Roundcube is accessible via http://roundcube.<domain>
- Lightweight client with a fluid interface
Accessing via Desktop
E-mail will be configured automatically if your desktop client supports Autodiscover/Autoconfig protocol. Only your e-mail address is necessary to for the client to setup incoming mail server, outgoing mail server, and authentication information. Certain e-mail clients like Mail on OS X and iPhone do not support third-party automatic configuration, but rather use a proprietary protocol and application. These devices require manual setup.
Automatic Setup
Mozilla Thunderbird
Setup under Mozilla Thunderbird will succeed automatically.
- Visit Tools > Account Settings
- Select Account Actions at the bottom
- Select Add Mail Account
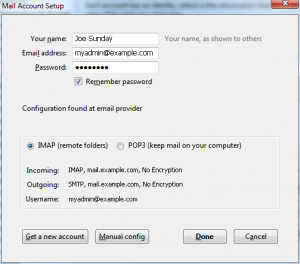
- Enter Your name, email address, and password, which is the same as your control panel password.
- Autoconfigure will succeed in detecting your settings. If autoconfig fails, skip to MANUAL CONFIGURATION below
- Click Done
- A security warning may pop-up. Click I understand the risks, then Done
- Congratulations, your mail account is setup!
Microsoft Outlook
Setup under Microsoft Outlook will succeed automatically.
- Visit File > Add Account
- Ensure E-mail Account is selected
- Enter Your name, e-mail address, and password, which is the same as your control panel password.
- A dialog titled, “Allow this website to configure XXX server settings?” will appear
- Additionally tick “Don’t ask me about this website again”
- Click Allow
- A password dialog will appear. Click Save this password in your password list
- Congratulations, your mail account is setup!
Manual Setup
Mozilla Thunderbird
- Follow the steps outlined in Automatic Setup above.
- Stop at Step 5 (autoconfig success). Click Manual Config
- Configure incoming mail server
- Select IMAP for Incoming server type
- Enter mail.yourdomain for Server Hostname – substitute yourdomain with your actual domain name
- Select Port 143
- Select None for SSL
- Select Normal Password for Authentication
- Configure outgoing mail server
- Select SMTP for Outgoing server type
- Enter mail.yourdomain for Server Hostname – substitute yourdomain with your actual domain name
- Select Port 587
- Select None for SSL
- Select Normal Password for Authentication
- Configure your username, which is your login
- Enter user@yourdomain substituting user with the user assigned to this e-mail account and yourdomain being your actual domain name
- Click Done
Other Mail Clients
Other mail clients may be setup in a similar fashion. Just keep these parameters in mind:
- Incoming and outgoing mail server are the same
- mail.yourdomain where yourdomain is your domain name
- e.g. an e-mail account for lithiumpanel.com would use the mail server mail.lithiumpanel.com
- mail.yourdomain where yourdomain is your domain name
- Select IMAP for incoming e-mail server type. IMAP allows multiple devices to access your e-mail and synchronize what e-mail has been read, replied to, and deleted
- Specify port 587 for outgoing e-mail
- Port 25 is discouraged, because mail servers relay mail through this port rather than mail clients submitting an e-mail. Likewise, ISPs typically restrict access on this port via firewall.
- Your login will always be user@yourdomain
- Your password will always be the same password used to access the control panel
Still having problems logging in?
If all of your credentials are correct, and your connection is not being blocked after 3 invalid requests in a 5 minute window, then 1 of 3 issues are to blame:
- Invalid password
- Solution: login to the control panel as the primary account holder. Visit User > Manage Users. Click the Edit action under the Actions column. Enter a new password for this user.If you access e-mail as the primary account holder, then you will be unable to login to the control panel if your password is invalid (e-mail and control panel use the same password source). Reset your password through the control panel reset utility.
- User denied IMAP/POP3 access
- Solution: this only happens with secondary users on the account. A user must be privileged to access the e-mail server to receive e-mail. Login to the control panel as the primary account holder.
- Visit User > Manage Users
- Verify that mail is not enabled for the user. The mail column will be empty.
- If a checkmark is present, then the user is accessing with incorrect credentials.
- Click the Edit action under the Actions column.
- Enable E-Mail under General Service Configuration
- If E-Mail is already enabled, click Advanced
- Verify that “User may login to IMAP/POP3 server” is also checked
- Solution: this only happens with secondary users on the account. A user must be privileged to access the e-mail server to receive e-mail. Login to the control panel as the primary account holder.
- Your DNS configuration points to an old provider
- Solution: try accessing e-mail by the server name. If you can login successfully, then DNS has yet to fully propagate yet. If you changed nameservers over 72 hours ago, verify the change went through by confirming with the company that manages your domain registration.